Slopes
From section 2.4, we know that the function to calculate the slope of a line can be found using the formula
In this above formula, represents the point at which we want to find the slope, and is an infinitesimally small distance away from .
Definition of the Derivative
For some continuous and differentiable at , the derivative is equal to
or alternatively at ,
Examples
The derivative of at :
Therefore,
The derivative of at :
Relating and
A horizontal line has a slope of zero. It follows that the derivative would be equal to zero.
For a other differentiable functions that are not completely horizontal throughout their domains, points where the slope is equal to zero are the roots of the derivative.
These zero points are local minima and maxima, where reaches a peak or trough. To find minima and maxima, identify the roots of the first derivative .
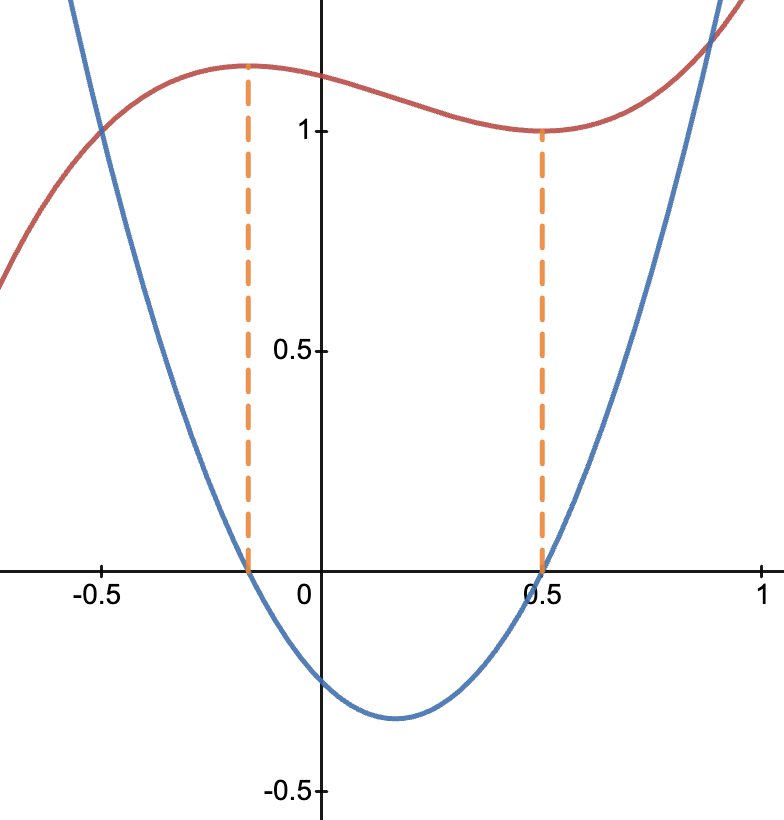 |
|---|
| A graphical representation |
Tangent Lines
The derivative at any point in the domain of is equal to the slope at .