Balance of Trade
The balance of trade refers to the gap between a nation’s exports and imports.
- A deficit occurs when more is imported than exported
- A surplus occurs when more is exported than imported
- Trade is balanced when imports and exports are equal
- Merchandise trade balance measured the trade of physical goods
- High-income economies have less physical trade
- Current account balance measures income flows and foreign aid
- The current account balance include the merchandise trade balance, payments for services, income payments (foreign investments), and unilateral transfers (aid, charity)
International Trade
Two key metrics for how globalized an economy is are:
- Goods and service exports as % of GDP
- Current account balance as % of GDP
Capital Flow
A trade surplus is equal to capital outflow, and deficit equal to inflow. The balance of trade can also be describe as the balance of payments.
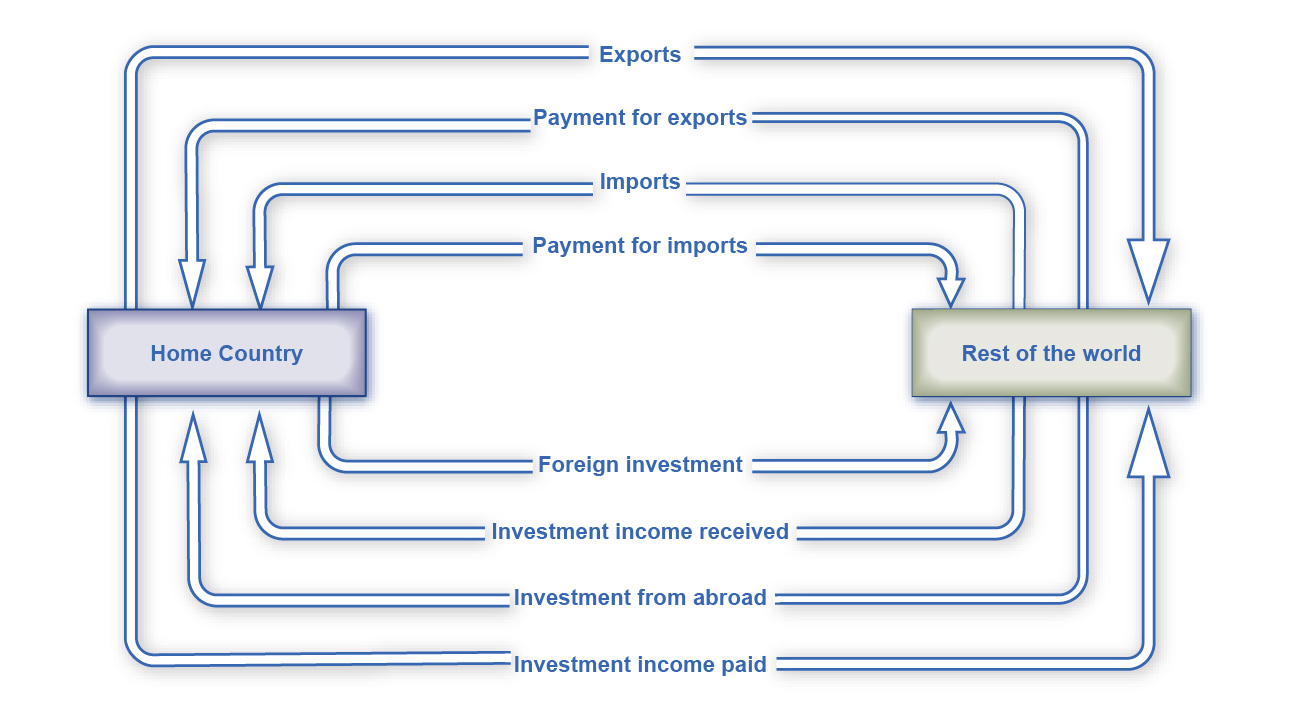 |
|---|
| A deficit does not strictly imply debt, as it could also be attributed to foreign investment. |
National Savings and Investment Identity
Capital supply is expressed as S + (M - X):
- S = savings
- (M - X) = capital flow/trade balance
- M = imports/inflow
- X = exports/outflow
Capital demand is expressed as I + (G - T)
- I = private investment
- (G - T) = government borrowing
- G = govt. spending
- T = tax income
The formula can be manipulated to isolate any one variable.
Short-Run Movements
Deficits tend to shrink or surpluses grow during recession, and vice versa during growth.
Pros and Cons of Trade Deficits
The pros of an economy running a deficit include:
- Borrowed capital can be used to make investments that increase productivity
- Growth from foreign investment can be used to repay debt and cause a surplus
Cons include:
- Capital invested in ways that do not increase productivity incurs significant interest
- Foreign investors can pull out quickly and cause a recession
Level of Trade vs. Trade Balance
Level of trade refers to the portion of GDP that can be attributed to the export of goods and services. It is also an indicator of how much of an economy’s production is exported. The level of trade is influenced by an economy’s size, location, and trade history.
Balance of trade refers to the imports of an economy compared to its exports.
A nation that exports a major share of its domestic production, meaning a high level of trade, can also run a deficit, such is the case of Canada.