Terminology
-
Experiment: a planned operation carried out under controlled conditions
- Chance experiment: outcome is not predetermined (flipping a fair coin)
- Outcome: the result of an experiment
- Sample space: all possible outcomes (sample space of a D6 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6})
- Event: any combination of outcomes
-
Long-term relative frequency: the probability of any outcome
- Probabilities are between 0 and 1 (inclusive)
-
Equally likely: each outcome occurs with equal probability
-
Law of large numbers: the empirical (observed) relative frequency of an outcome tends to the its theoretical probability over a large number of repetitions
Notation for Probability
- : outcomes
- OR : outcomes OR or both
- AND : outcomes AND
- Complement : all outcomes NOT in
- Conditional : given
| Probability | Venn Diagram |
|---|---|
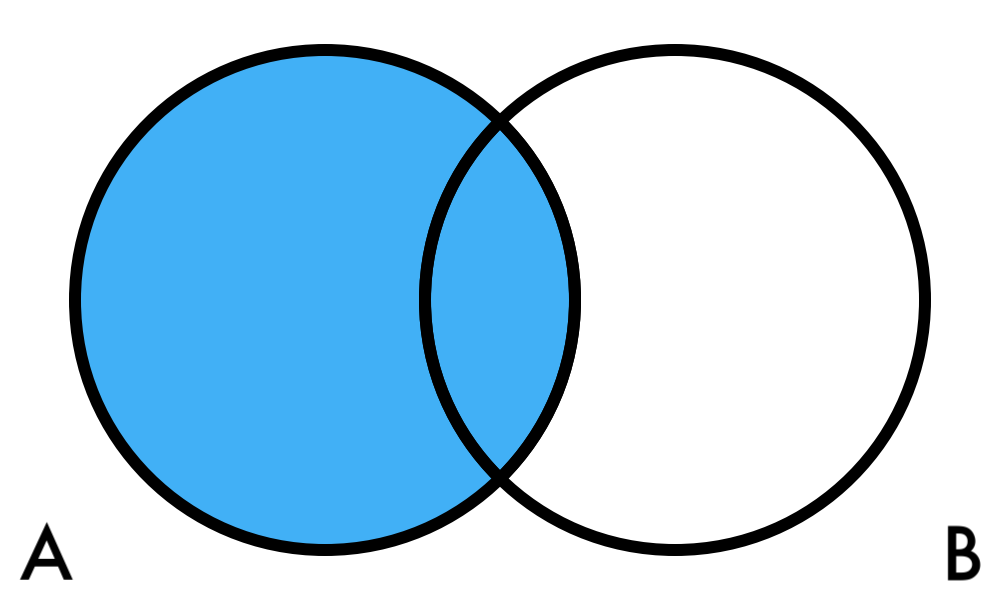 | |
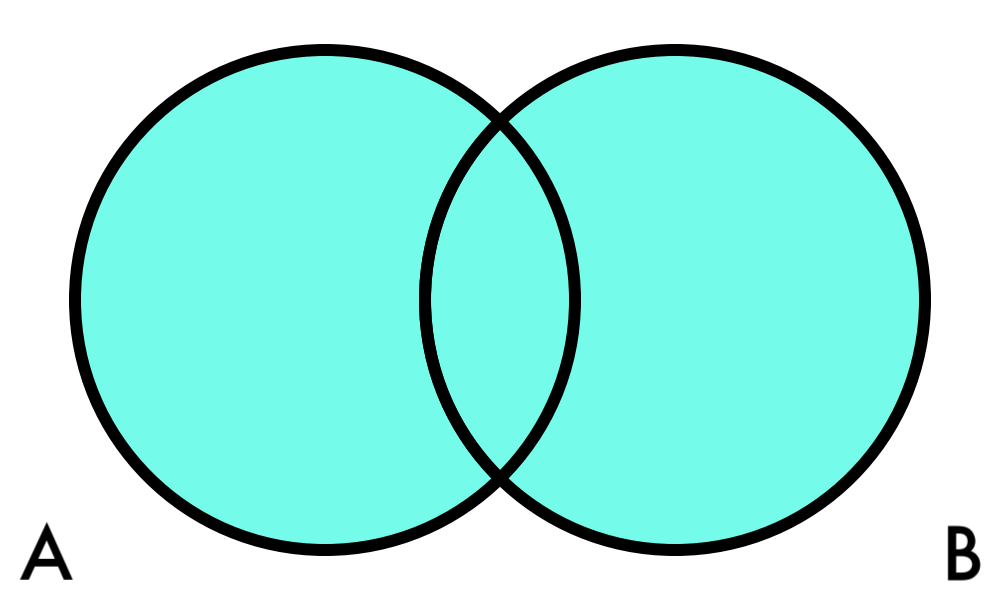 | |
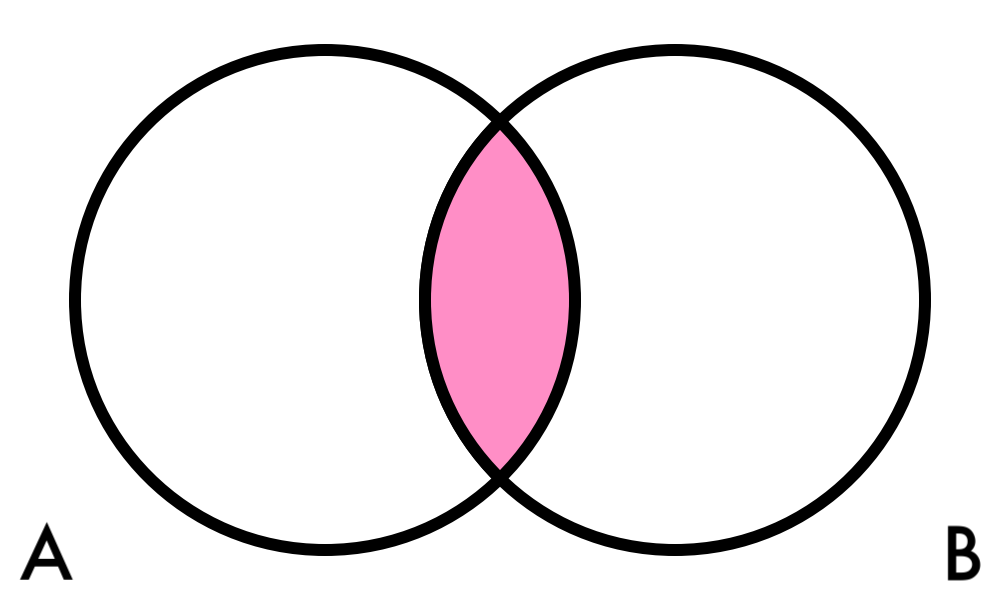 |
Independent and Mutually Exclusive Events
Independent Events
Two events are independent if:
This simply means that knowledge of one event will not affect the other.
Assume events are dependent until proven otherwise.
Mutually Exclusive Events
Two events are mutually exclusive if:
This means they cannot occur at the same time. Assume events are not mutually exclusive until proven otherwise.
Two Basic Rules
Multiplication Rule
When and and are independent:
Addition Rule
When and are mutually exclusive:
Contingency Tables
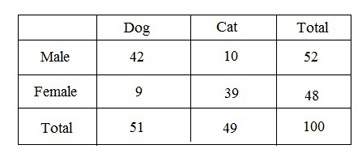 |
|---|
- Examples:
Tree and Venn Diagrams
Tree Diagrams
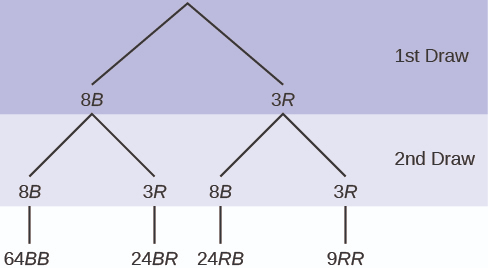 |
|---|
| (with replacement) |
The final stage of the tree diagram represents the frequencies of all outcomes, which are out of 121 (64 + 24 + 24 + 9 = 121).
- Examples:
- ( also calculated as from the reduced sample space)
Venn Diagrams
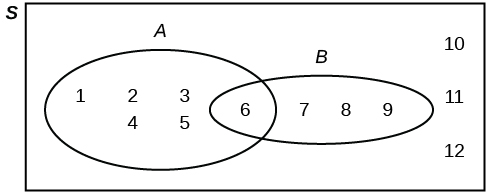 |
|---|
-
-
-
-
-
Examples:
Example
2% of a population of dogs have a disease. There is a test dogs can take for the disease. If a dog has the disease, the test will have a positive result 95% of the time. If the dogs does not have the disease, the test will have a positive result 12% of the time.
What is the probability a dog has a positive test?
Give that a dog tests positive, what is the probability that it actually has the disease?